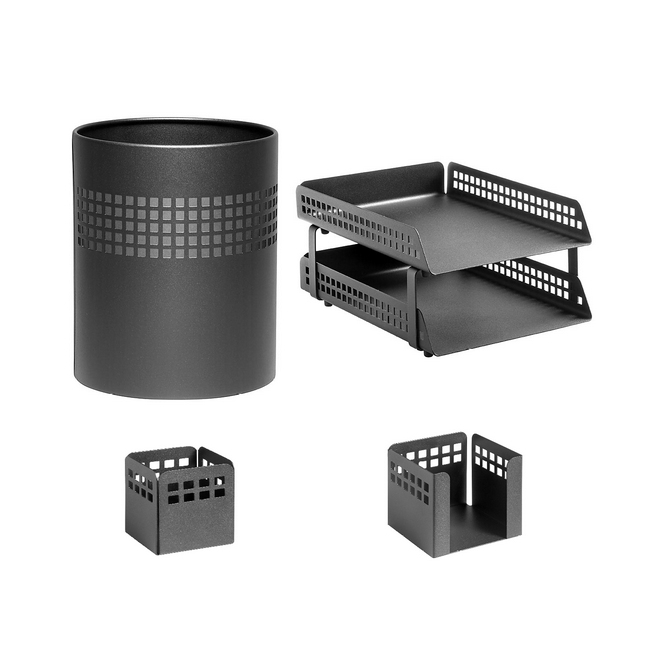
Desk Set – Square Punch Steel Range – Metal – Letter Tray – Waste Bin – Pencil Cube and Cup – Colour Options – 413BL
R2,773.00 Ex VAT
- Material: Metal
- Includes: Letter tray, waste bin, pencil cube and pencil cup
- Tier: Double tier
- External dimensions per tray: 350 x 250 x 65 mm
- External dimensions for both trays: 350 x 250 x 170 mm
- Colour options
- Item delivery usually within 2 weeks