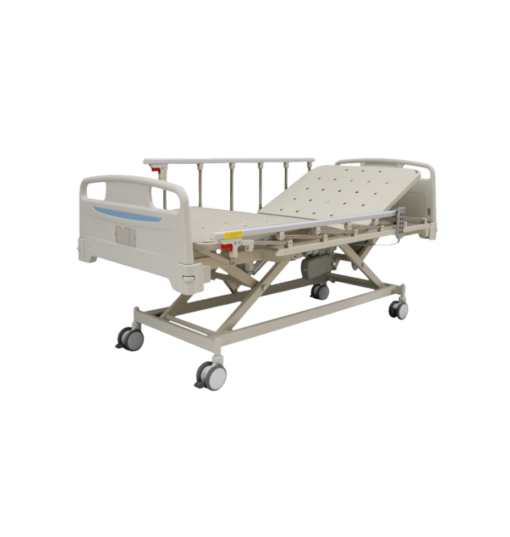
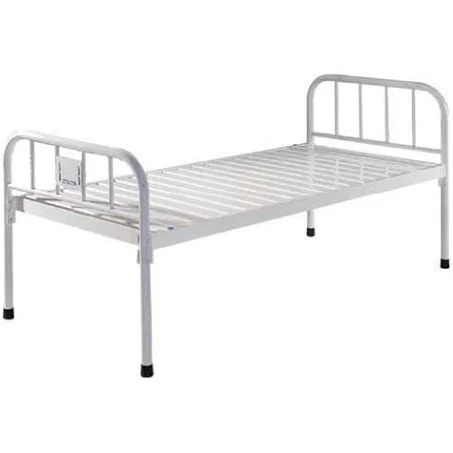
hospital beds for sale in south africa
R7,050.00 Ex VAT
hospital beds for sale in south africa
Category: Uncategorized
Tag: hospital beds for sale in south africa
Hospital beds are designed to provide comfort, support, and safety for patients while allowing healthcare providers to deliver effective care. There are several types of hospital beds, each with specific features and uses. Here are the main types and their uses:
1. Manual Hospital Beds
- Description: Operated using hand cranks to adjust the bed’s height and position.
- Uses: Suitable for facilities with limited budgets or where power outages are common. Often used in home care settings.
2. Semi-Electric Hospital Beds
- Description: Combine manual and electric features. Electric controls adjust the head and foot sections, while a manual crank adjusts the bed height.
- Uses: Provide a balance of convenience and cost-effectiveness. Common in both home care and medical facilities.
3. Fully Electric Hospital Beds
- Description: All adjustments (height, head, and foot sections) are made using electric controls.
- Uses: Ideal for both hospitals and home care, especially for patients who need frequent position changes.
4. Low Hospital Beds
- Description: Can be lowered close to the floor to reduce the risk of falls.
- Uses: Suitable for patients at high risk of falling, such as the elderly or those with mobility issues.
5. Bariatric Hospital Beds
- Description: Designed to support heavier patients, typically with wider frames and higher weight capacities.
- Uses: For bariatric patients in both hospital and home care settings, providing additional strength and durability.
6. Gatch Beds
- Description: Older style, typically manual, with three adjustments: head, foot, and height.
- Uses: Found in less modernized facilities or in situations where cost is a significant factor.
7. Stretchers/Gurney Beds
- Description: Mobile beds used for transporting patients within a facility.
- Uses: Common in emergency rooms, operating rooms, and for patient transport.
8. Low Air Loss Beds
- Description: Equipped with air-filled mattresses that can adjust the pressure to reduce skin breakdown.
- Uses: Ideal for patients at high risk of pressure ulcers (bed sores), often used in intensive care units (ICUs).
9. Fluidized Air Beds
- Description: Utilize a fluid-like substance under the mattress cover to reduce pressure on the patient’s skin.
- Uses: For patients with severe skin conditions or pressure ulcers, often in specialized care units.
10. Clinitron Beds
- Description: A type of fluidized air bed that provides an optimal healing environment by reducing pressure and maximizing comfort.
- Uses: For patients with extensive burns, pressure sores, or other skin conditions requiring a high level of care.
11. Rotating/Turning Beds
- Description: Can rotate or turn patients automatically to prevent pressure sores and improve circulation.
- Uses: For immobilized patients who need regular repositioning but cannot move independently.
12. Specialty Beds
- Description: Includes various beds designed for specific medical conditions or procedures, such as cardiac beds or pediatric beds.
- Uses: Tailored to the unique needs of specific patient groups or medical treatments.
Each type of hospital bed is designed with particular features to address different patient needs and care settings. The selection of the appropriate bed type depends on factors such as patient condition, care environment, and budget.
Related products
Uncategorized
R195.00 Ex VAT
Uncategorized
R1,900.00 Ex VAT
Uncategorized
R32,594.00 Ex VAT
Uncategorized
R650.00 Ex VAT
Uncategorized
R16,544.00 Ex VAT
R32,610.00 Ex VAT
Uncategorized
R32,598.00 Ex VAT
Uncategorized
R32,590.00 Ex VAT