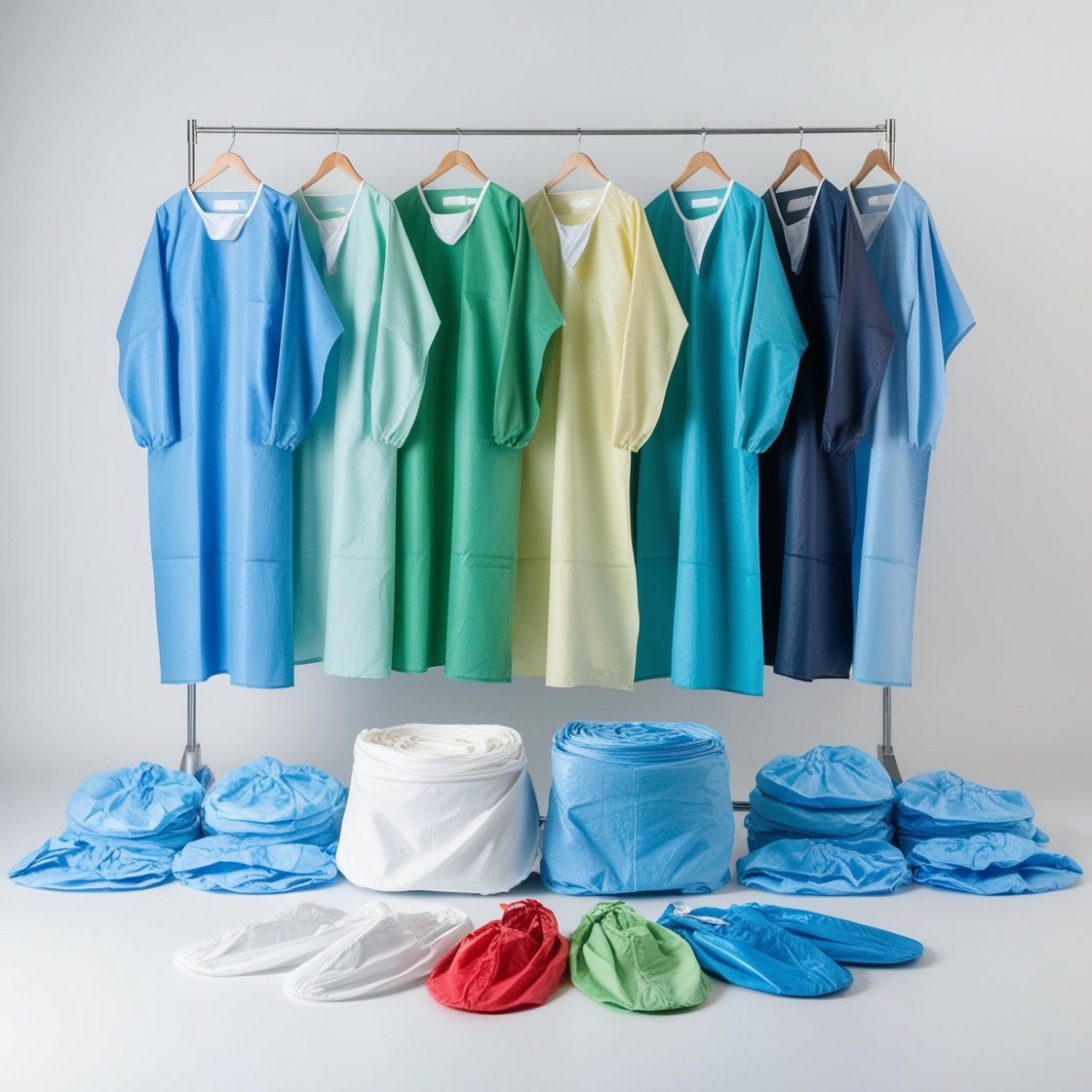
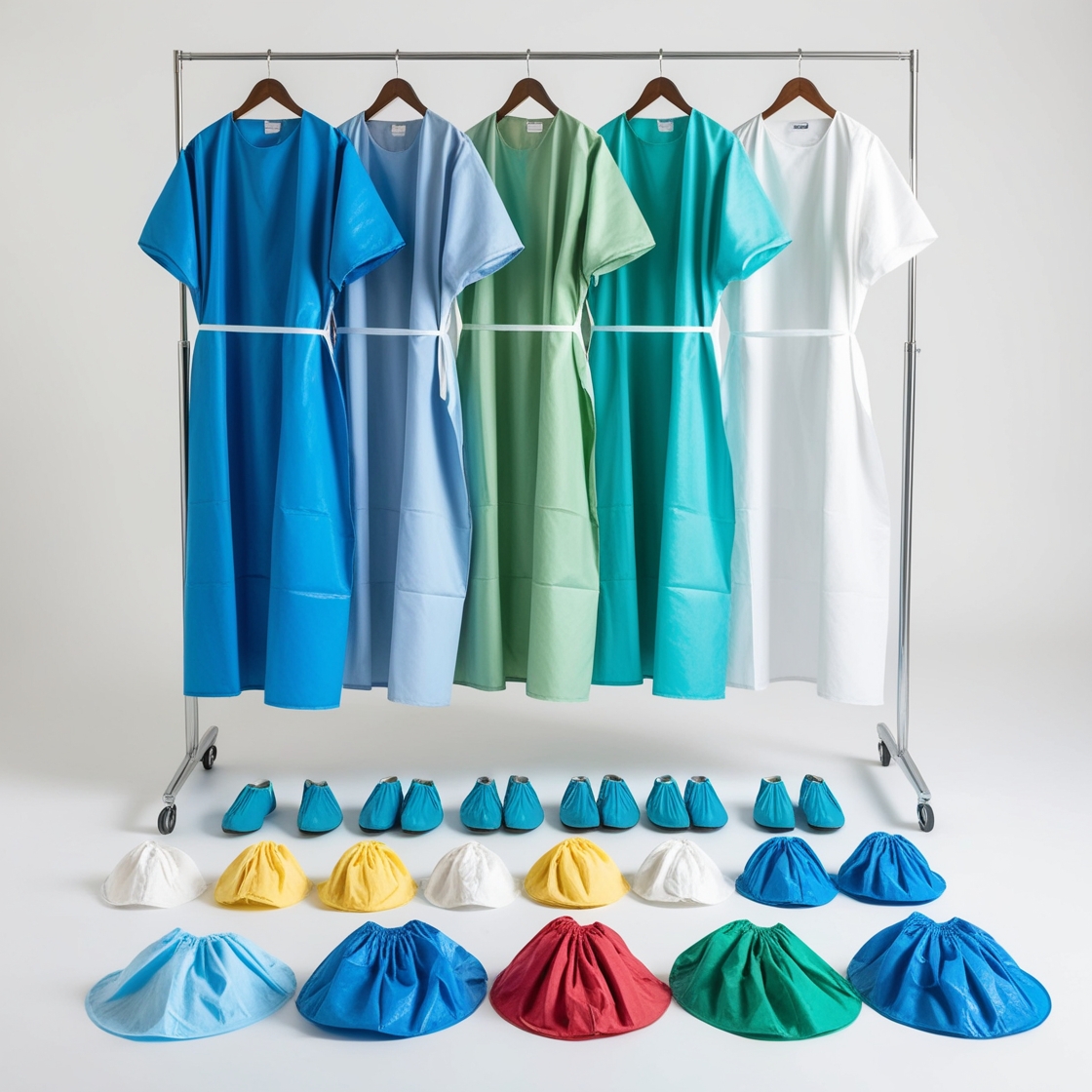
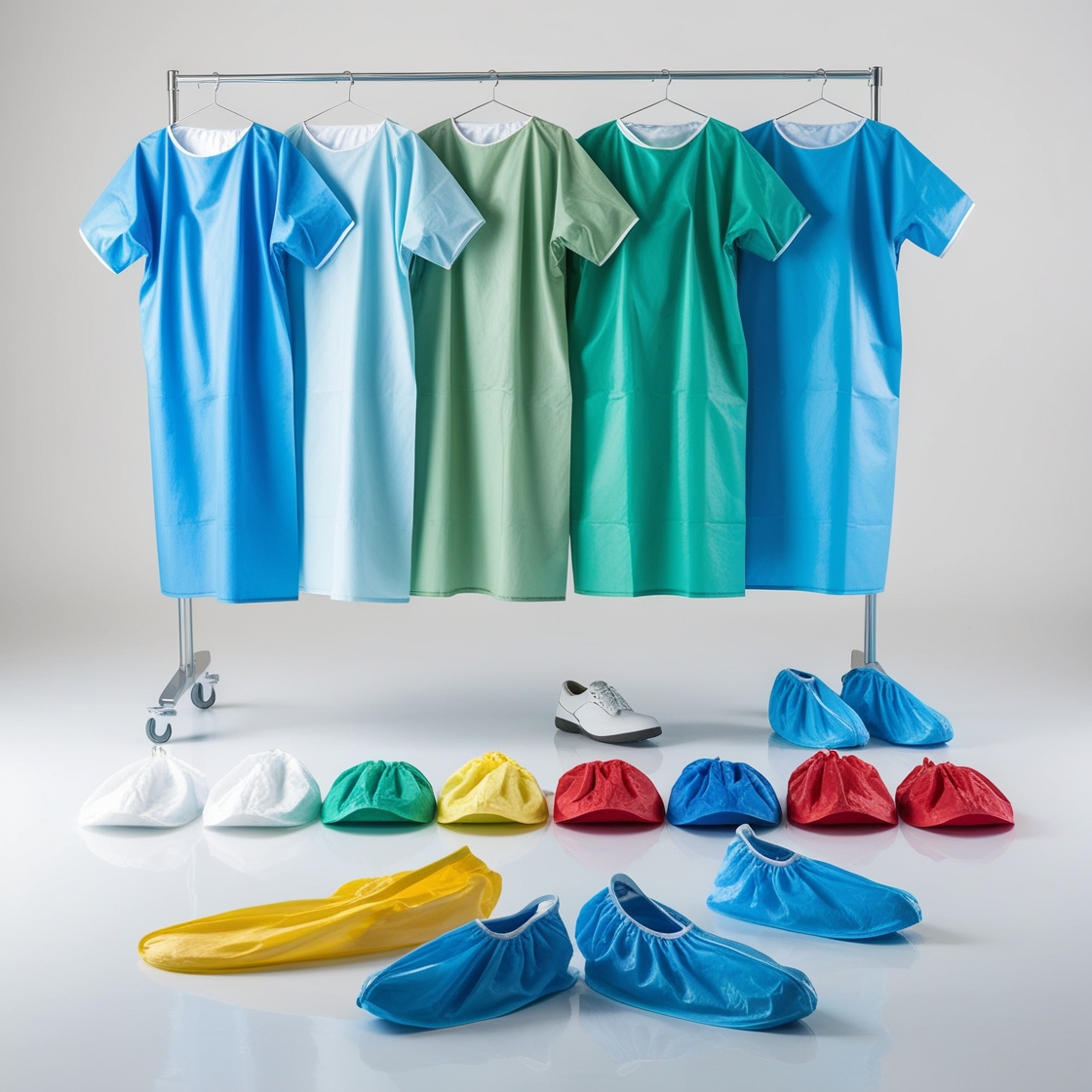
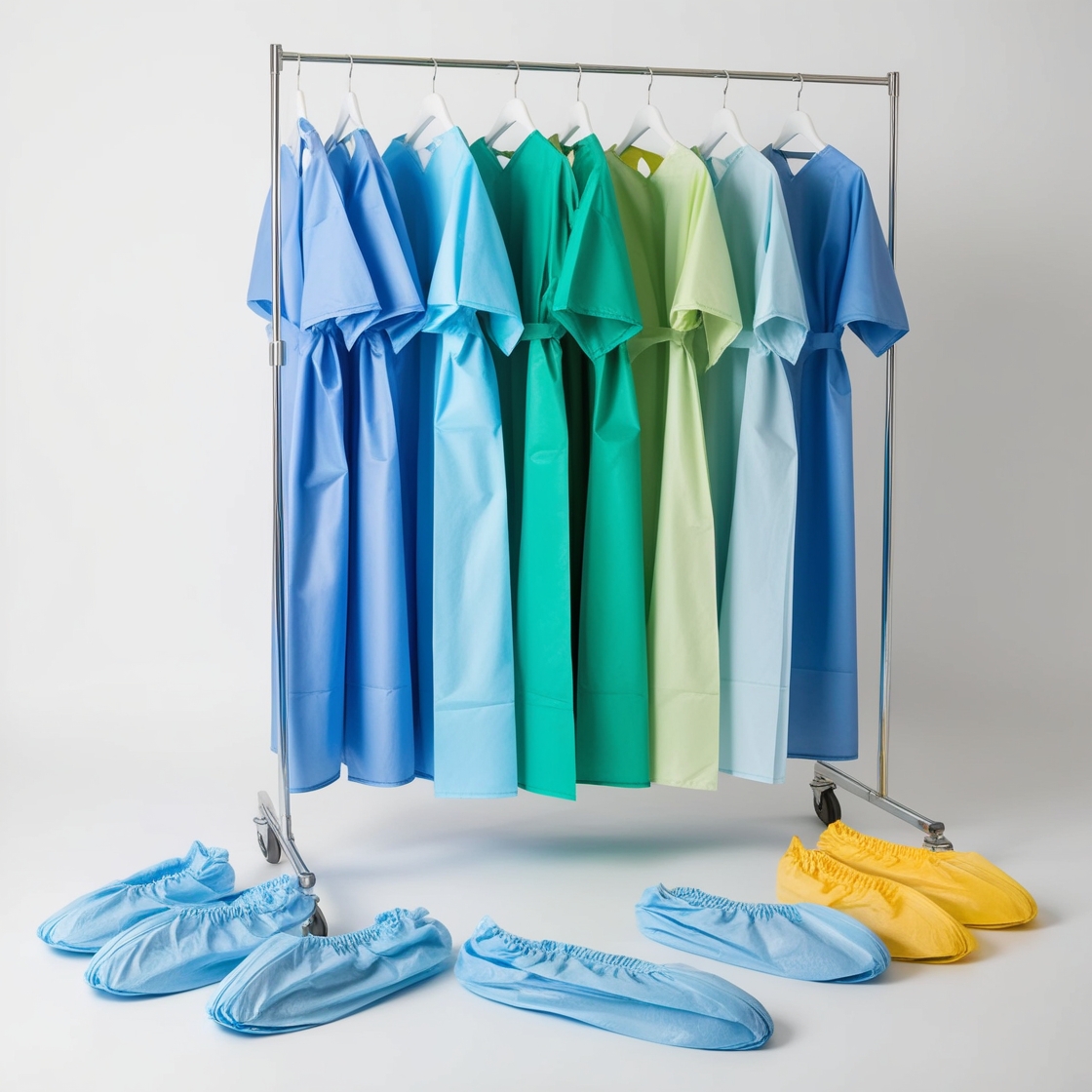
disposable isolation gowns
R29.00 Ex VAT
Hospital gowns are essential garments designed to protect both patients and healthcare providers from contamination and provide comfort during medical procedures. There are various types of hospital gowns, each tailored for specific medical uses and levels of protection. Below are the main types of hospital gowns and their uses:
1. Patient Gowns
- Description: These are lightweight, loose-fitting gowns typically worn by patients during hospital stays or medical examinations. They are usually open in the back and secured with ties or Velcro.
- Uses:
- Worn by patients during surgeries, diagnostic procedures, or hospital admissions.
- Designed for ease of access for medical staff and comfort for the patient.
- Used in settings where basic patient modesty and hygiene are required, such as hospitals, clinics, and outpatient centers.
2. Surgical Gowns
- Description: Surgical gowns provide a high level of protection against fluid and pathogen exposure during surgical procedures. They are sterile, fluid-resistant, and often made from reinforced materials like polypropylene or polyester.
- Uses:
- Worn by surgeons, surgical assistants, and other operating room staff.
- Protects healthcare providers from exposure to blood, bodily fluids, and pathogens during surgery.
- Used in sterile environments such as operating rooms and during invasive procedures.
3. Isolation Gowns
- Description: Isolation gowns are protective garments designed to protect both patients and healthcare workers from the transmission of infectious diseases. These gowns are made from materials that resist fluids and are available in varying levels of protection.
- Uses:
- Used in settings where patients have or are suspected of having infectious diseases.
- Commonly worn by healthcare workers in emergency rooms, intensive care units (ICUs), and during patient examinations in infectious disease wards.
- Protects against contact with infectious agents, including bacteria and viruses.
4. Disposable Gowns
- Description: Disposable gowns are single-use garments made from lightweight materials like non-woven polypropylene or polyethylene. These gowns are typically fluid-resistant or fluid-impermeable.
- Uses:
- Used in situations where contamination risk is high, and reusing a gown is not practical.
- Commonly worn in surgical settings, isolation units, and laboratories.
- Ideal for healthcare workers who need to frequently change gowns between patients or procedures to prevent cross-contamination.
5. Reusable Gowns
- Description: Reusable gowns are made from durable, washable fabrics like cotton or polyester, designed to be laundered and reused multiple times.
- Uses:
- Used in hospitals, clinics, or home care settings where cost-effectiveness and sustainability are prioritized.
- Suitable for general patient care and low-risk environments.
- Offers protection against minimal exposure to fluids and contaminants, with lower levels of protection compared to disposable gowns.
6. Procedural Gowns
- Description: These gowns are designed for non-surgical medical procedures where exposure to moderate fluid is expected. They provide mid-level protection and are made from materials that resist fluid penetration.
- Uses:
- Worn by healthcare workers during non-invasive procedures, such as endoscopy, radiology, or catheterization.
- Offers protection from splashes or fluid contact during diagnostic tests and minor procedures.
7. Chemotherapy Gowns
- Description: Chemotherapy gowns are specialized gowns that offer high levels of protection against hazardous drugs used in chemotherapy treatments. These gowns are made from materials resistant to chemotherapy agents.
- Uses:
- Worn by nurses, oncologists, and pharmacists who handle or administer chemotherapy drugs.
- Provides protection from accidental exposure to hazardous drugs during preparation, administration, and disposal.
- Common in oncology departments, chemotherapy clinics, and pharmaceutical preparation areas.
8. Lead Apron Gowns
- Description: Lead apron gowns are heavy, lead-lined garments designed to protect healthcare workers from radiation exposure during diagnostic imaging procedures like X-rays.
- Uses:
- Worn by radiologists, dental technicians, and other healthcare providers who work with radiographic equipment.
- Shields the body from harmful radiation during procedures involving X-rays, CT scans, and fluoroscopy.
- Used in radiology departments, dental offices, and interventional radiology.
9. Maternity Gowns
- Description: Maternity gowns are designed specifically for pregnant women in labor and delivery settings. They provide comfort, modesty, and easy access for medical staff during childbirth and postpartum care.
- Uses:
- Worn by expectant mothers during labor, delivery, and postpartum recovery.
- Features front openings or panels for easy access during examinations and breastfeeding.
- Used in maternity wards and birthing centers to provide comfort and convenience.
10. Exam Gowns
- Description: Exam gowns are simple, disposable or reusable gowns worn by patients during medical examinations. They are typically lightweight and provide basic coverage.
- Uses:
- Used by patients during routine physical exams, diagnostic tests, or outpatient visits.
- Provides easy access to specific parts of the body for examination while maintaining patient modesty.
- Common in doctor’s offices, outpatient clinics, and diagnostic labs.
11. Pediatric Gowns
- Description: Pediatric gowns are designed specifically for children and infants, providing smaller sizes and sometimes featuring fun designs to make the hospital experience less intimidating for young patients.
- Uses:
- Worn by children during hospital stays, surgeries, or medical procedures.
- Helps comfort young patients and maintain modesty during treatment.
- Common in pediatric wards, children’s hospitals, and emergency rooms.
12. Level 1 Isolation Gowns
- Description: These gowns provide minimal protection and are used in situations with a low risk of fluid exposure. Level 1 isolation gowns are lightweight and comfortable, offering basic protection.
- Uses:
- Worn in environments where there is minimal risk of exposure to body fluids.
- Used in routine care settings, such as during patient examinations or routine check-ups.
- Suitable for use in non-critical areas of hospitals or clinics.
13. Level 2 Isolation Gowns
- Description: Level 2 gowns offer moderate protection against fluid penetration. These gowns are used in environments where there is a higher risk of exposure to body fluids but not in surgical settings.
- Uses:
- Used in healthcare environments where low to moderate fluid contact is anticipated, such as in the ICU or emergency departments.
- Worn by healthcare workers who may come into contact with blood or bodily fluids during procedures like inserting IV lines or drawing blood.
14. Level 3 Isolation Gowns
- Description: Level 3 isolation gowns provide a higher level of fluid and particulate protection. They are designed for use in moderate-risk environments with significant fluid exposure potential.
- Uses:
- Worn during procedures where moderate to high fluid exposure is expected, such as during arterial blood draws or trauma care.
- Provides more protection than Level 1 or Level 2 gowns and is used in more invasive procedures or critical care settings.
15. Level 4 Isolation Gowns
- Description: Level 4 gowns provide the highest level of protection and are impermeable to fluids and bacteria. They are often used in high-risk environments.
- Uses:
- Worn during major surgical procedures and in environments where there is a high risk of exposure to infectious materials or large amounts of bodily fluids.
- Provides maximum protection for healthcare workers handling highly infectious patients or involved in critical procedures.
16. Radiation Protection Gowns
- Description: Radiation protection gowns are designed with lead or other radiation-blocking materials to protect healthcare workers from exposure during radiation-based diagnostic procedures.
- Uses:
- Worn by radiologists, technicians, and other healthcare workers involved in X-ray and other radiology procedures.
- Common in imaging centers, hospitals, and dental offices to protect staff from radiation.
17. Disposable Sterile Gowns
- Description: These gowns are made for one-time use in sterile environments, such as operating rooms. They are fluid-resistant and sterile, reducing the risk of infection during procedures.
- Uses:
- Worn by surgical teams during invasive procedures to maintain a sterile environment.
- Helps prevent cross-contamination between healthcare workers and patients.
- Used in sterile surgical environments, such as operating theaters and labor rooms.
18. Infection-Control Gowns
- Description: These gowns are designed to reduce the spread of infections in healthcare environments. They are typically fluid-resistant and disposable to prevent contamination.
- Uses:
- Worn in environments where infection control is crucial, such as infectious disease wards or isolation units.
- Used by healthcare workers to prevent the transmission of infections like MRSA, tuberculosis, or COVID-19.
19. Emergency Room Gowns
- Description: These gowns provide ease of use and quick access for medical staff during emergency treatments. They are fluid-resistant and designed for fast changes during trauma care.
- Uses:
- Worn by patients and staff in emergency rooms, where rapid access and frequent changes are necessary.
- Used in high-stress environments where trauma and injury care require quick response times and protection.
20. Critical Care Gowns
- Description: Critical care gowns provide high levels of protection for healthcare workers in intensive care units (ICU). They are often fluid-resistant or fluid-impermeable.
- Uses:
- Worn by nurses, doctors, and other staff in ICUs to prevent