Foldable examination bed (couch)
R3,800.00 Ex VAT
Description:
1. Adjustable backrest.
2. Foam-padded.
3. Mounted on protective stumps.
Dimensions: 190cm(L) 65cm (W) 70cm (H)
Weight: 25kg
Foldable Examination Bed/Adjustable Backrest
- Patient safety is ensured whilst being treated as legs stay locked
- Multi-positioning, double ratchet backrest ensures patient can be fully examined in comfort
- Multiple applications and situations can be handled with the height adjustment
- Double layered, high grade density, 2in foam upholstery is available number of different colours
Examination bed rectangular steel tube frame, powder-coated RAL 9002, RAL 9006 or RAL 9007, 2-section 50 mm thick foam rubber upholstery, leveling feet, head section adjustable up to +40°. Safe working load: 225 kg. This examination couch has a black upholstered top with an adjustable backrest. fixed-height,
Adjustable Headrest
Fold-away legs with braces to stabilize legs
Rubber grommets
Size : 1865mm L x 610mm W
Height: 830mm Unfolded, 200mm Folded
Weight : 15.5 kg
Nose hole, Hand towel rail, and Castors optional
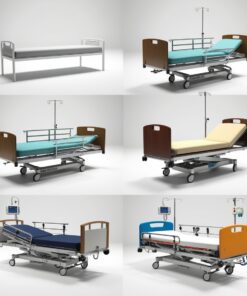
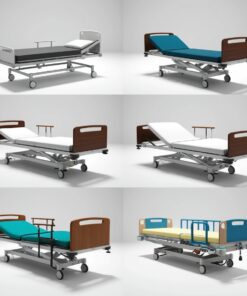
Hospital beds are specialized medical devices designed to accommodate patients during treatment or recovery. They provide comfort, safety, and support for patients while offering functionality to caregivers for effective medical care. There are various types of hospital beds, each designed for specific medical needs. Here are the main types and their uses:
1. Manual Hospital Beds
- Description: These beds are adjusted manually using hand cranks. The caregiver adjusts the bed’s height, head, and foot positioning by turning the cranks.
- Uses:
- Suitable for healthcare facilities or home care where budget constraints are a concern.
- Used for patients who need occasional adjustments and do not require frequent repositioning.
- Common in low-resource settings or as temporary beds in hospitals.
2. Semi-Electric Hospital Beds
- Description: These beds have an electric motor to control the head and foot adjustments, but the height is adjusted manually using a hand crank.
- Uses:
- Suitable for patients who need to frequently adjust their head or foot positioning for comfort or medical reasons.
- Often used in home care settings or hospitals with moderate budget constraints.
- Provides more convenience than a manual bed but is less costly than fully electric models.
3. Electric (Full-Electric) Hospital Beds
- Description: These beds are fully motorized, allowing adjustments to the bed’s height, head, and foot sections through electric controls (usually via a remote or a panel on the bed).
- Uses:
- Ideal for hospitals and home care settings where patients require frequent repositioning.
- Beneficial for patients with limited mobility, as they can adjust their position independently.
- Reduces caregiver effort in manually adjusting the bed, especially in busy hospital environments.
4. ICU (Intensive Care Unit) Beds
- Description: ICU beds are highly advanced, fully electric beds equipped with several features to support critically ill patients. They often include in-built monitors, ventilator supports, and alarms.
- Uses:
- Designed for critically ill patients who require constant monitoring and frequent position adjustments.
- Used in intensive care units (ICU) to support patients with severe medical conditions.
- Often have features like built-in scales, lateral rotation, CPR functionality, and trendelenburg/reverse trendelenburg positioning (head or feet higher than the body).
5. Low Hospital Beds
- Description: These beds are designed to be low to the ground, making it easier for patients to get in and out of bed, especially those prone to falling.
- Uses:
- Commonly used for elderly patients or those at high risk of falling.
- Suitable for patients with limited mobility or those recovering from surgery who need to minimize the risk of injury from falls.
- Often used in geriatric care or rehabilitation centers.
6. Bariatric Hospital Beds
- Description: These beds are designed to accommodate heavier patients, offering a larger width and greater weight capacity (often up to 500 kg or more).
- Uses:
- Ideal for obese patients requiring specialized care.
- Equipped with reinforced frames and wider mattresses to provide comfort and safety for larger patients.
- Used in hospitals and healthcare facilities specializing in bariatric care or long-term care facilities.
7. Low Air Loss Beds
- Description: These beds have air-filled mattresses with continuous airflow, reducing pressure points on the patient’s skin.
- Uses:
- Used for patients at high risk of developing bedsores (pressure ulcers).
- Common in long-term care facilities or for immobile patients who need pressure relief to maintain skin integrity.
- Beneficial for patients with spinal injuries, paralysis, or conditions requiring long periods of bed rest.
8. Alternating Pressure Beds
- Description: These beds use air chambers that alternately inflate and deflate, shifting the pressure on different parts of the body to avoid prolonged pressure on any one area.
- Uses:
- Designed for patients with or at risk of bedsores (pressure ulcers).
- Used in long-term care facilities, hospices, and home care for bedridden patients.
- Helps prevent the development of pressure sores by continuously redistributing pressure.
9. Stryker or Stretchers Hospital Beds
- Description: These are specialized mobile beds with wheels, used to transport patients between hospital departments or for emergency room use.
- Uses:
- Common in emergency departments, operating rooms, and trauma centers for moving patients quickly.
- Used for patient transport within hospitals or in ambulances.
10. Gatch Beds
- Description: Older, mechanical beds adjusted manually through three cranks at the foot of the bed (one for raising the head, one for raising the foot, and one for adjusting height).
- Uses:
- Historically common but now often replaced by electric beds.
- Still used in low-resource hospitals and home care settings where electric beds are not feasible.
- Used for basic patient care where frequent adjustments are not needed.
11. Trendelenburg Hospital Beds
- Description: These beds allow the patient to be positioned with their feet elevated higher than their head (Trendelenburg position) or the reverse (Reverse Trendelenburg position).
- Uses:
- Frequently used in surgery or trauma care to improve blood flow to vital organs.
- Beneficial for patients with respiratory or circulatory problems.
- Often used in ICU or surgical settings to provide enhanced patient care.
12. Pediatric Hospital Beds
- Description: These beds are specifically designed for children, often featuring side railings, a smaller size, and colorful designs to create a more comforting environment.
- Uses:
- Ideal for pediatric wards and children’s hospitals.
- Used to care for infants and young patients, providing safety features that prevent falls or injuries.
- Commonly equipped with adjustable side rails and child-friendly controls.
13. Rehabilitation Beds
- Description: These are specialized beds designed for patients undergoing rehabilitation, particularly for those who need help with mobility or transferring in and out of bed.
- Uses:
- Used in rehabilitation centers or long-term care facilities.
- Ideal for patients recovering from strokes, spinal cord injuries, or major surgeries.
- Often equipped with side rails, trapeze bars, and adjustable height to aid in patient mobility and rehabilitation exercises.
Additional Features of Hospital Beds:
- Side Rails: Provide safety by preventing patients from falling out of bed.
- Mattress Type: Can include foam, air-filled, or gel mattresses to cater to patient comfort and medical needs.
- Adjustability: Allows for the head, feet, or the entire bed to be raised or lowered for patient comfort and medical procedures.
- Built-in Scales: Some hospital beds come with integrated weighing scales to monitor patient weight without moving them.
Conclusion:
The type of hospital bed selected depends on the patient’s medical condition, mobility, and care requirements. From manual to fully electric beds, each type offers specific features and advantages tailored to various patient care scenarios.
Related products
Examination bed
Examination bed
Examination bed
Examination bed
Disposable Gloves
Examination bed
Examination bed
Examination bed